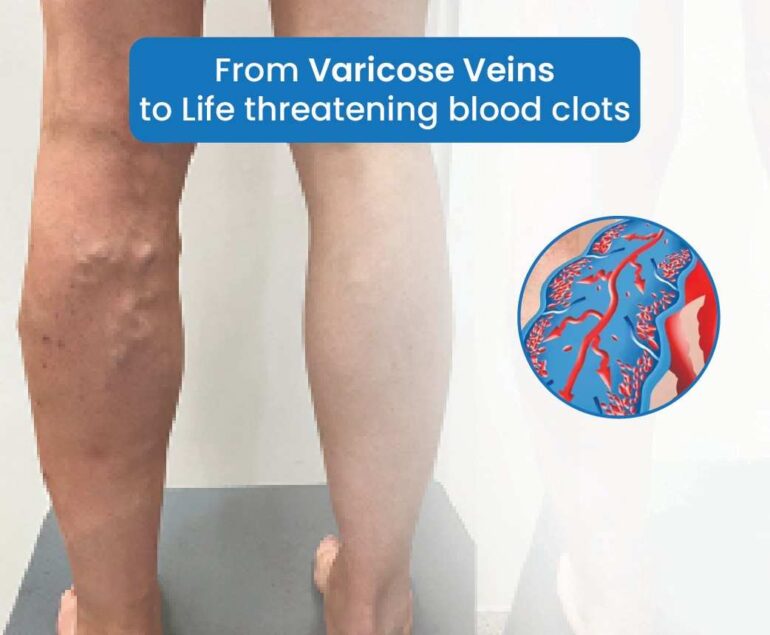
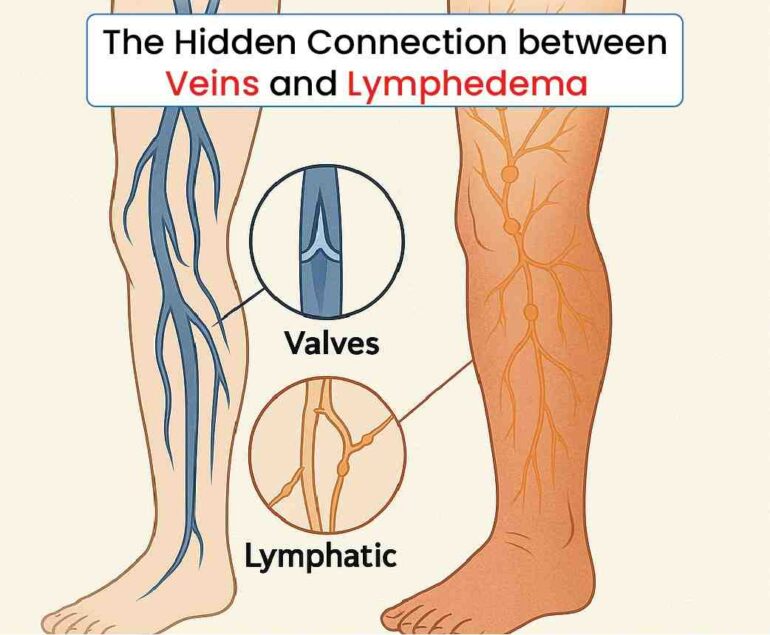
Thyroid nodules are lumps that commonly form within the thyroid gland, located at the base of the neck. While many thyroid nodules are benign and asymptomatic, their presence can sometimes lead to significant health concerns. Understanding the nature of these nodules, their potential consequences, and the benefits of treatment options like ablation is crucial for managing thyroid health effectively.
What are Thyroid Nodules?
Thyroid nodules are abnormal growths of thyroid cells that form lumps in the thyroid gland. These nodules can vary in size, ranging from tiny, barely detectable lumps to large masses that can be felt or seen as a swelling in the neck. They can be solid, filled with fluid, or a combination of both.
Causes and Risk Factors
Several factors can contribute to the development of thyroid nodules, including:
- Iodine Deficiency: A lack of iodine in the diet is a known risk factor.
- Genetic Predisposition: A family history of thyroid nodules or thyroid cancer increases the likelihood.
- Radiation Exposure: Previous exposure to radiation, particularly to the head and neck area, can increase risk.
- Age and Gender: Thyroid nodules are more common in women and older adults.
Symptoms and Potential Consequences
Many thyroid nodules are asymptomatic and are often discovered during routine physical exams or imaging studies conducted for other reasons. However, when symptoms do occur, they can include:
- Visible Swelling: A noticeable lump or swelling in the neck.
- Difficulty Swallowing or Breathing: Large nodules can press on the esophagus or windpipe.
- Voice Changes: Hoarseness or voice changes may occur if a nodule compresses the vocal cords.
- Hyperthyroidism or Hypothyroidism: Some nodules produce thyroid hormones, leading to hyperthyroidism, while others can cause hypothyroidism by interfering with normal thyroid function.
While most thyroid nodules are benign, a small percentage can be malignant. Thus, it is essential to evaluate and monitor any thyroid nodules to rule out thyroid cancer.
Diagnosis and Evaluation
To assess thyroid nodules, healthcare providers typically perform:
- Physical Examination: Checking for lumps and evaluating symptoms.
- Ultrasound: Imaging to determine the size, composition, and characteristics of the nodules.
- Fine-Needle Aspiration Biopsy: Collecting cells from the nodule to check for cancerous changes.
- Blood Tests: Evaluating thyroid function and hormone levels.
Ablation of Thyroid Nodules
Ablation therapy has emerged as an effective treatment option for managing certain types of thyroid nodules, particularly those that are benign but symptomatic or cosmetically concerning. There are different types of ablation techniques, including:
- Radiofrequency Ablation (RFA): Uses heat generated by radiofrequency energy to destroy the nodule tissue.
- Ethanol Ablation: Involves injecting ethanol directly into the nodule to induce shrinkage.
- Laser Ablation: Uses laser energy to heat and reduce the size of the nodule.
Benefits of Ablation
Ablation offers several advantages over traditional surgical approaches:
- Minimally Invasive: Ablation procedures are typically less invasive than surgery, resulting in smaller or no incisions.
- Reduced Recovery Time: Patients often experience quicker recovery times and fewer complications.
- Preservation of Thyroid Function: Unlike thyroidectomy (surgical removal of the thyroid), ablation preserves the thyroid gland, maintaining its hormone-producing function.
- Cosmetic Benefits: Ablation can reduce the size of visible nodules, improving cosmetic concerns without the need for a larger surgical scar.
Thyroid nodules are a common thyroid disorder that can lead to significant health issues if not appropriately managed. While many nodules are benign and asymptomatic, others can cause symptoms and require intervention. Ablation therapy offers a minimally invasive, effective treatment option, preserving thyroid function and improving patient outcomes. If you suspect you have a thyroid nodule, consult a healthcare provider for appropriate evaluation and management. With advancements in treatment options like ablation, patients can achieve better health and quality of life while addressing their thyroid concerns.