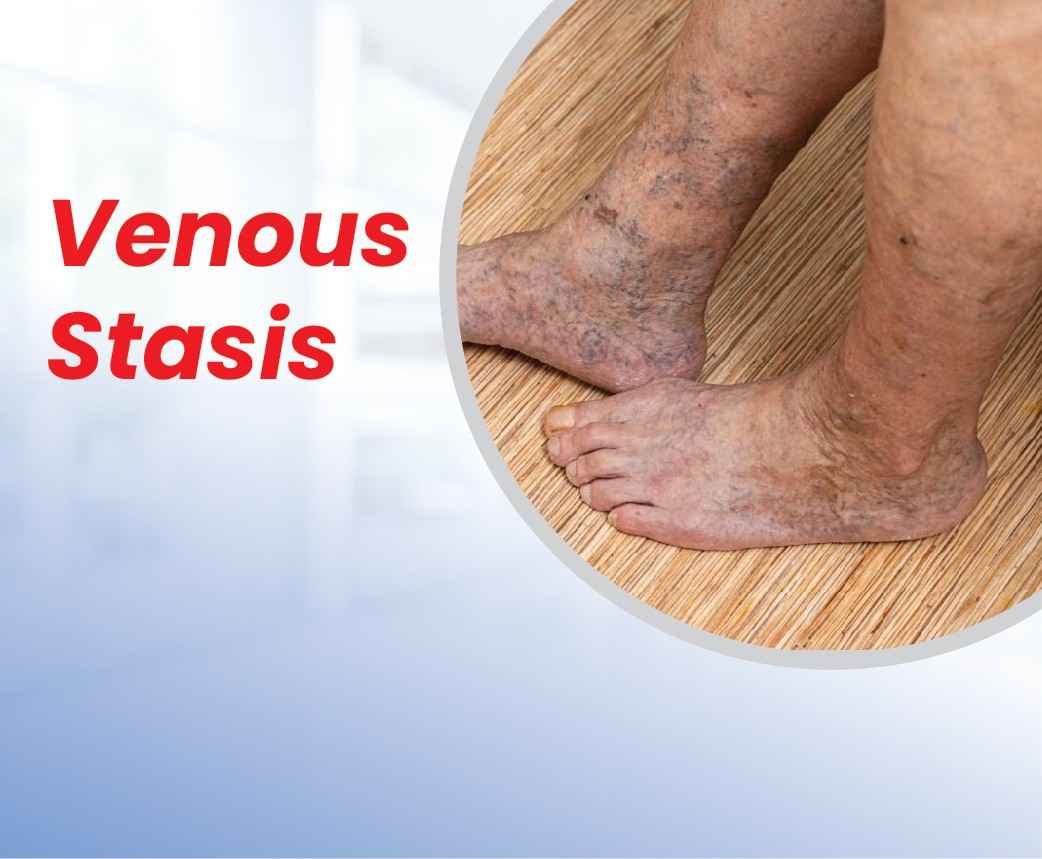
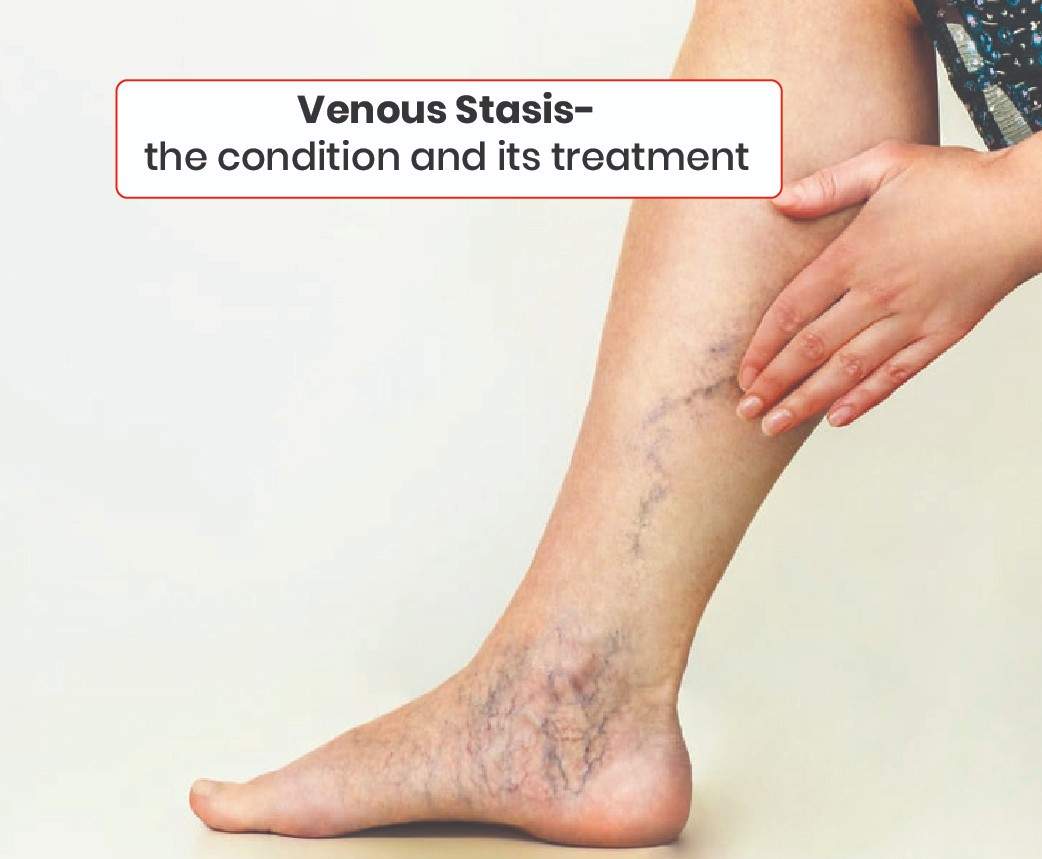
Venous stasis, also known as venous insufficiency, is a common circulatory condition affecting millions worldwide. This condition occurs when the veins in your legs struggle to efficiently pump blood back to your heart, leading to blood pooling in the lower extremities. While traditionally managed through surgical interventions, modern medicine now offers less invasive yet highly effective treatment options that have revolutionized patient care.
Understanding the Mechanism
The human circulatory system relies on one-way valves within veins to prevent blood from flowing backward as it travels upward against gravity. When these valves become damaged or weakened, blood can flow backward and pool in the legs, leading to venous stasis. This condition is particularly common in the deep veins of the legs, affecting people of various ages and backgrounds. Several factors contribute to developing venous stasis, including age (over 50), obesity, prolonged sitting or standing, pregnancy, family history, previous blood clots, and smoking.
Warning Signs
The initial manifestations of venous stasis often begin subtly but progressively worsen if left unaddressed. Patients typically first notice a persistent heaviness or aching in their legs, particularly after long periods of standing. This discomfort often intensifies as the day progresses. Swelling, known as edema, usually starts around the ankles and may gradually extend upward.
Many individuals experience an uncomfortable itching or tingling sensation in their legs, which can become particularly bothersome during evening hours. Leg cramps, especially during night time, are another common complaint that can significantly disturb sleep patterns. The skin may begin to show changes, starting with a subtle darkening or reddish discoloration. Some patients report a feeling of restlessness in their legs, compelling them to move frequently for relief. These symptoms typically worsen in warm weather or after prolonged periods of inactivity.
Complications
When venous stasis progresses without proper intervention, it can lead to several serious complications that significantly impact a patient’s quality of life. The most concerning is the development of venous ulcers, which typically appear near the ankles where blood pooling is most severe.
These ulcers are notoriously painful and resistant to healing, often requiring specialized wound care and prolonged treatment. The compromised circulation also makes the affected areas highly susceptible to cellulitis, a potentially serious bacterial skin infection that can spread rapidly if not treated promptly.
Deep Vein Thrombosis (DVT) becomes a significant risk as the sluggish blood flow creates ideal conditions for clot formation. These clots can be life-threatening if they break loose and travel to the lungs. Over time, patients may develop lipodermatosclerosis, where the skin and underlying fat become hardened and inflamed, leading to further discomfort and complications. The chronic pain associated with these complications can be debilitating, affecting mobility, sleep, and overall quality of life.
Prevention and Management
Successful management of venous stasis requires a comprehensive approach that combines lifestyle modifications with medical interventions. Regular physical activity, particularly walking and leg-strengthening exercises, plays a crucial role in improving circulation and preventing blood pooling. It’s essential to maintain a healthy weight, as excess pounds put additional pressure on the venous system. Patients should avoid prolonged periods of sitting or standing and take frequent breaks to move around or elevate their legs.
Compression therapy, through properly fitted stockings, remains a cornerstone of management, helping to prevent swelling and improve blood flow. Adequate hydration is vital, as it helps maintain proper blood viscosity and circulation. Elevating the legs above heart level whenever possible, especially during rest periods, can significantly reduce swelling and discomfort. Regular follow-up with healthcare providers is essential to monitor the condition’s progression and adjust treatment plans as needed. Patients should also be vigilant about skin care to prevent complications, using moisturizers to prevent dryness and watching for any signs of skin breakdown or infection.