Lymphedema, a chronic condition characterized by the swelling of limbs due to a compromised lymphatic system, can significantly impact a person’s quality of life. The persistent swelling, discomfort, and risk of infections make managing this condition a daily challenge. While lymphedema is primarily associated with the lymphatic system, there is a strong connection between the health of your veins and the severity of lymphedema symptoms. Understanding and addressing underlying vein issues can be a crucial step in alleviating the burden of lymphedema.
The Interplay Between Veins and the Lymphatic System
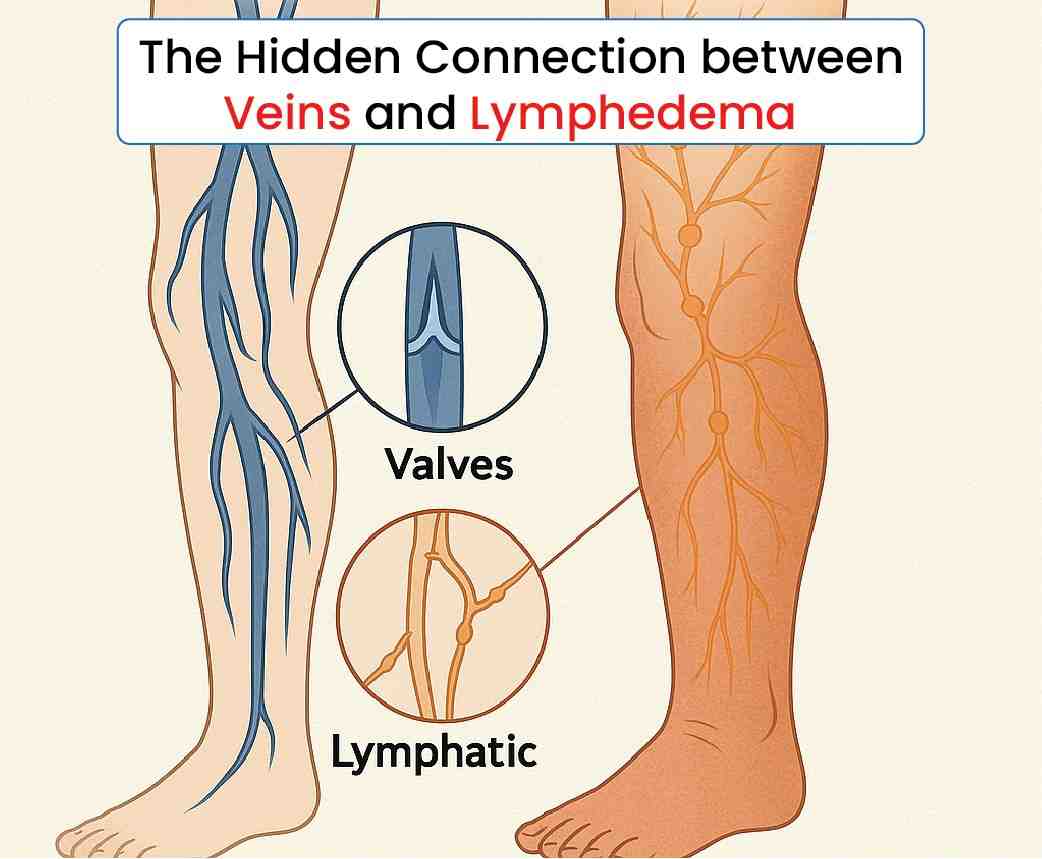
The venous and lymphatic systems are two critical components of your body’s circulatory network, working closely to maintain fluid balance. The veins are responsible for returning deoxygenated blood back to the heart, while the lymphatic system helps drain excess fluid, proteins, and waste products from the tissues, directing them into the bloodstream. When either system is compromised, the other often struggles to compensate, leading to fluid buildup and swelling.
In individuals with chronic venous insufficiency (CVI), the veins fail to efficiently return blood to the heart. This failure allows blood to pool in the lower extremities, increasing pressure in the veins and causing fluid to leak into surrounding tissues. This fluid accumulation can overwhelm the lymphatic system, which is already compromised in people with lymphedema, resulting in increased swelling and discomfort.
Treating Vein Issues to Ease Lymphedema Symptoms
Addressing vein problems can be a significant part of managing lymphedema symptoms. Here’s why:
- Reducing Fluid Accumulation: Treating venous insufficiency can help reduce the amount of fluid that leaks into the tissues, alleviating the burden on the lymphatic system. This reduction in fluid buildup can lead to less swelling, making lymphedema easier to manage.
- Improving Circulation: Better vein function improves overall circulation, ensuring that both blood and lymph fluid are more effectively transported and drained from the affected areas. This can lead to a noticeable reduction in the heaviness and discomfort associated with lymphedema.
- Lowering the Risk of Complications: By addressing underlying vein issues, the risk of complications like skin infections (cellulitis) and ulcers is reduced. Improved circulation helps maintain healthier skin and tissues, which are less prone to injury and infection—a common concern in lymphedema patients.
- Enhanced Lymphedema Therapies: When venous health is improved, other lymphedema treatments such as compression therapy, manual lymphatic drainage, and exercise can become more effective. This holistic approach can help in achieving better outcomes in managing lymphedema symptoms.
How Are Vein Issues Treated?
Treating vein issues, particularly chronic venous insufficiency, can involve several approaches. Compression therapy is often the first line of defense, using specially designed garments to help improve blood flow in the legs and reduce swelling. For more severe cases, minimally invasive procedures such as sclerotherapy, endovenous laser treatment (EVLT), or radiofrequency ablation may be recommended. These treatments work by closing off or removing damaged veins, which redirects blood flow through healthier veins, improving overall circulation and reducing symptoms.
Conclusion
Lymphedema management often requires a multifaceted approach, and addressing vein health can play a crucial role in this process. By treating underlying venous issues, you can reduce the severity of lymphedema symptoms, making the condition more manageable and improving your overall quality of life. If you or someone you know is struggling with lymphedema, it may be worthwhile to explore the connection between vein health and symptom severity with your healthcare provider. With the right treatment plan, you can take meaningful steps toward reducing the impact of lymphedema on your daily life.